Understanding Cellulitis: Diagnosis and Care

Recognizing cellulitis early can be the key to effective treatment and recovery. With knowledge about this bacterial skin infection, you can take proactive steps to protect your skin health. Here’s what you will learn about cellulitis and its implications.
What You Will Learn
- Cellulitis is caused by bacteria entering through breaks in the skin, often requiring prompt treatment to prevent complications.
- Common symptoms include swelling, redness, pain, and fever, which should be monitored closely for timely medical intervention.
- Risk factors for developing cellulitis include skin conditions, a compromised immune system, obesity, and diabetes.
- Understanding the role of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus can help in preventing and managing cellulitis effectively.
- Complications from cellulitis may include recurrent infections, lymphedema, and in rare cases, osteomyelitis, highlighting the need for careful monitoring.
- Chronic cellulitis can occur due to underlying health issues, necessitating ongoing communication with healthcare providers for effective management.
- The psychological impact of cellulitis can affect self-esteem and lead to anxiety, making mental health support an important aspect of recovery.
Key Aspects of Cellulitis: Symptoms, Risk Factors & Bacteria
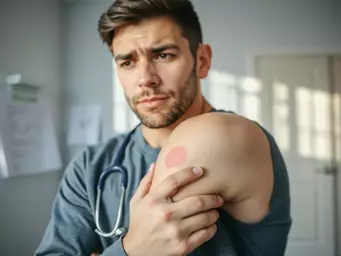
Cellulitis is a serious bacterial skin infection. Understanding its symptoms, who is at risk, and the bacteria responsible is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
Common Symptoms
- Swelling: Inflamed area
- Redness: Spreading area
- Pain: Tenderness to touch
- Fever: Body's response
Key Risk Factors
- Skin Conditions: Eczema, athlete's foot
- Compromised Immune System: Higher susceptibility
- Obesity: Moisture trapping skin folds
- Diabetes: Impaired infection fight
Causative Bacteria
- Staphylococcus aureus: Common on skin, invades via breaks
- Streptococcus: Can cause rapid, expanding infection
Potential Complications
- Recurrent infections: Increased susceptibility
- Lymphedema: Fluid buildup, swelling
- Abscess formation: Pus requiring drainage
- Osteomyelitis: Bone infection (rare)
Understanding Cellulitis: A Common Bacterial Skin Infection
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can affect anyone, often causing worry due to its potential severity. At What Are Rashes, we aim to demystify this condition and empower you with knowledge about its implications on your skin health. By understanding cellulitis, you can recognize symptoms early and seek timely treatment, which is crucial for effective management.
In this section, we'll explore what cellulitis is, its symptoms, risk factors, and the bacteria commonly responsible for this infection. Let’s dive deeper into these important topics!
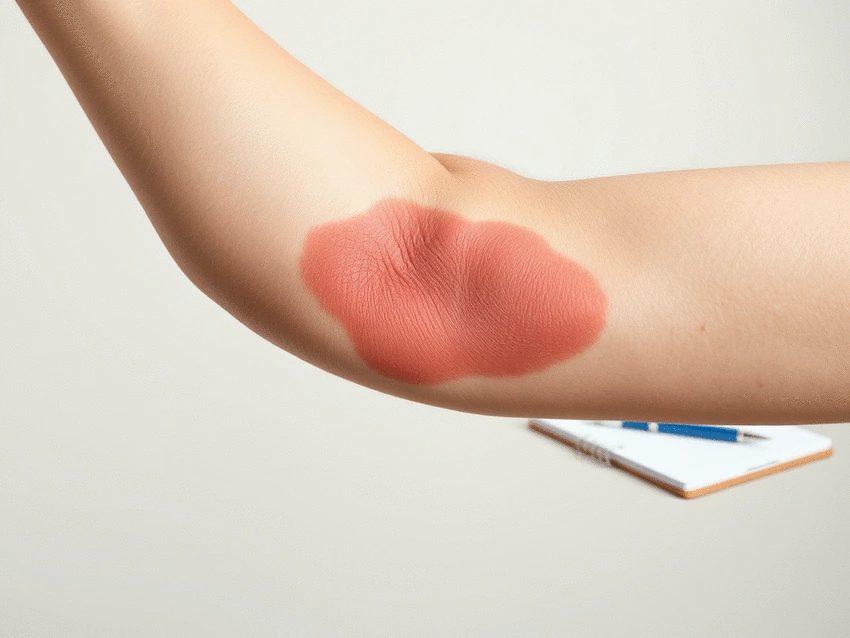
What Exactly is Cellulitis?
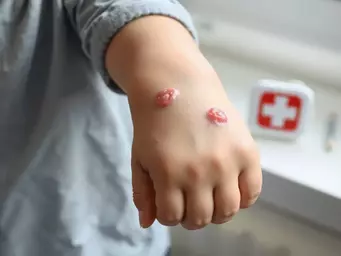
Cellulitis occurs when bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus, enter through breaks in the skin. This infection typically manifests in the deeper layers of the skin and can lead to significant discomfort. If left untreated, cellulitis can spread rapidly, underscoring the importance of understanding its nature.
- Bacterial Entry: Bacteria enter through cuts, surgical wounds, or insect bites.
- Common Areas Affected: It usually occurs on the legs, arms, or face.
- Potential Spread: The infection can spread to lymph nodes and bloodstream, leading to serious complications, as detailed by the CDC's clinical guidance on cellulitis.
Recognizing the nature of cellulitis is essential for anyone looking to maintain healthy skin. It’s vital to treat any minor cuts or wounds promptly to help prevent such infections.
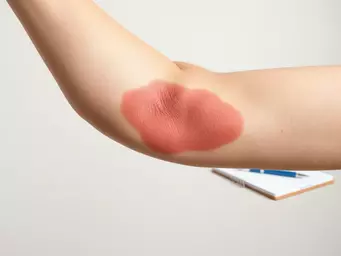
Common Symptoms and Clinical Presentation of Cellulitis
The symptoms of cellulitis can vary but often include noticeable signs that require attention. Common symptoms are:
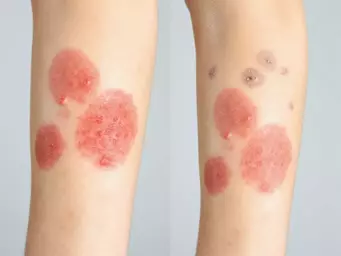
- Swelling: The affected area often becomes swollen and visibly inflamed.
- Redness: You may notice a spreading area of redness around the infection site.
- Pain: Pain or tenderness in the area can increase with touch.
- Fever: Many patients develop a fever as the body's response to infection.
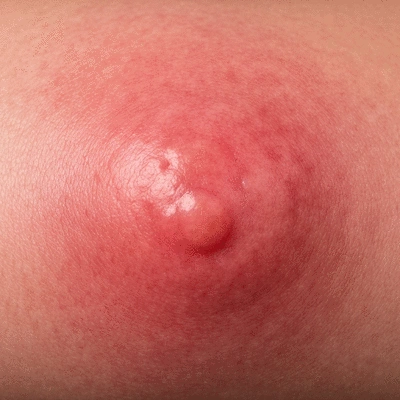
If you observe these symptoms on your skin, it's important to seek medical advice promptly. Early intervention can make a significant difference in your recovery journey, as highlighted by resources like the Mayo Clinic's guidelines for cellulitis diagnosis and treatment.
Identifying Risk Factors for Developing Cellulitis
Understanding the risk factors associated with cellulitis can help you take preventative measures. Here are some key factors:
- Skin Conditions: Eczema, athlete's foot, and other skin conditions can increase risk.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems are at higher risk.
- Obesity: Excess weight can lead to skin folds that trap moisture and bacteria.
- Diabetes: This condition can impair the body's ability to fight infections.
By identifying these risks, you can take proactive steps to maintain your skin health. Regular skin care and monitoring for any changes can help keep infections like cellulitis at bay.
The Role of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus in Cellulitis
Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus are the leading culprits behind cellulitis. These bacteria can thrive in environments where skin is broken or damaged. Understanding their roles can better prepare you for prevention.
- Staphylococcus aureus: Often found on the skin, it can invade through cuts or abrasions.
- Streptococcus: This bacterium can cause rapid cellulitis, often starting as a small red area that expands quickly. The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) provides comprehensive practice guidelines for skin and soft tissue infections, including those caused by these bacteria.
Through collaboration with dermatologists, we at What Are Rashes emphasize the importance of recognizing the signs of infection triggered by these bacteria. Keeping the skin intact and healthy is your best defense!
Clinical Approaches to Diagnosing Cellulitis
Diagnosing cellulitis requires a thorough evaluation by healthcare professionals. In the following sections, we will discuss how cellulitis is diagnosed and what key criteria are considered.
Pro Tip
Did you know? Keeping your skin moisturized can significantly reduce the risk of developing cellulitis, especially if you have skin conditions like eczema or athlete's foot. Regularly applying a good moisturizer helps maintain your skin barrier, making it less susceptible to bacterial infections.
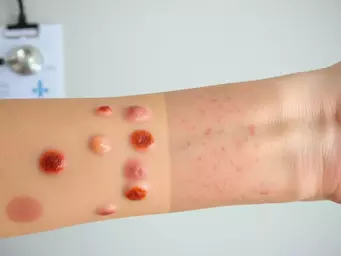
Understanding the Long-Term Impact of Cellulitis
While cellulitis is primarily known as a skin infection, its consequences can last well beyond the initial treatment. Many individuals may not realize the potential for long-term complications that can arise after an infection. Understanding these impacts is key to managing your health effectively.
After cellulitis, some patients may experience persistent swelling, pain, or changes in skin texture. These symptoms can drastically affect daily life, and it’s essential to be aware of them. Let’s explore the potential complications that may follow a cellulitis infection.
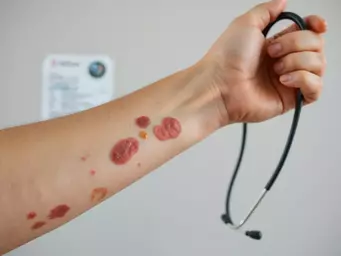
Potential Complications and Sequelae Following Infection
Complications from cellulitis can vary in severity and duration. Some common complications include:
- Recurrent infections: Once you’ve had cellulitis, you may be more susceptible to future infections.
- Lymphedema: This is when lymph fluid builds up in the tissues, leading to swelling, particularly in the limbs.
- Abscess formation: Sometimes, an area of pus can form, requiring drainage.
- Osteomyelitis: In rare cases, the infection can spread to the bones, necessitating more extensive treatment.
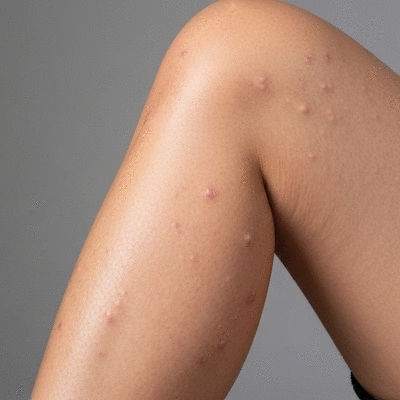
It’s crucial to monitor your recovery and report any unusual symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly. Early intervention can help address these complications before they worsen.
Psychological Impact of Dealing with Cellulitis
Dealing with a skin infection like cellulitis isn't just a physical challenge; it can also take a toll on your mental health. Many individuals find themselves grappling with anxiety or low self-esteem due to visible skin changes.
Feeling isolated or worried can be just as debilitating as the physical symptoms. Here are some common psychological effects:
- Fear of recurrence: Many worry that the infection will come back, leading to heightened anxiety.
- Body image issues: Changes in skin appearance can affect self-confidence.
- Social withdrawal: Fear of judgment may lead individuals to avoid social interactions.
Recognizing these feelings is an important step toward coping. Speaking to a mental health professional can provide you with strategies to manage anxiety and improve your outlook.
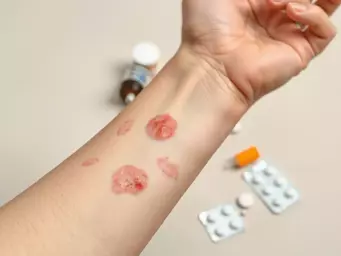
Chronic Cellulitis: Causes and Management
In some cases, patients may experience chronic cellulitis, where symptoms persist or recur frequently. Understanding the causes behind this can help in effective management.
Chronic cellulitis can be triggered by several factors, including:
- Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immunity may find it harder to fend off infections.
- Underlying health conditions: Conditions like diabetes or obesity can increase the risk of developing chronic cellulitis.
- Poor wound healing: If your body struggles to heal from injuries, this can lead to recurrent infections.
Managing chronic cellulitis often involves a comprehensive approach, including proper wound care, lifestyle changes, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers. Remember, you’re not alone in this; there are resources available to help you navigate your recovery.
FAQ: Understanding Cellulitis
Here are some frequently asked questions to help you better understand cellulitis:
- Q: What is cellulitis?
- A: Cellulitis is a common bacterial skin infection that causes redness, swelling, and pain in the affected area. It occurs when bacteria enter through a break in the skin.
- Q: What are the common symptoms of cellulitis?
- A: Common symptoms include swelling, spreading redness, pain or tenderness to touch, and sometimes fever. It's important to seek medical attention if you notice these signs.
- Q: Who is at risk of developing cellulitis?
- A: Individuals with skin conditions (like eczema or athlete's foot), a compromised immune system, obesity, or diabetes are at higher risk.
- Q: Which bacteria typically cause cellulitis?
- A: The primary culprits are Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus bacteria, which invade through skin breaks.
- Q: Can cellulitis lead to long-term complications?
- A: Yes, if left untreated or recurring, it can lead to complications such as recurrent infections, lymphedema (fluid buildup), abscess formation, and rarely, osteomyelitis (bone infection).
- Q: How can I prevent cellulitis?
- A: Preventing cellulitis involves good skin hygiene, promptly cleaning and treating cuts or wounds, keeping skin moisturized, and managing underlying health conditions like diabetes.
Preparing for Your Healthcare Appointment
As you prepare for your appointment, it’s essential to come equipped with questions and a clear understanding of your symptoms. This can empower you to take control of your health journey.
Recap of Key Points
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
- Understanding Cellulitis: Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection primarily caused by Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus that enters through breaks in the skin.
- Common Symptoms: Symptoms include swelling, redness, pain, and fever. Early recognition is crucial for effective treatment.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with skin conditions, compromised immune systems, obesity, or diabetes are at higher risk of developing cellulitis.
- Potential Complications: Complications can include recurrent infections, lymphedema, abscess formation, and in rare cases, osteomyelitis.
- Psychological Impact: The infection can affect mental health, causing anxiety and body image issues due to visible skin changes.
- Management Strategies: Proper wound care, lifestyle changes, and ongoing communication with healthcare providers are essential for managing chronic cellulitis.