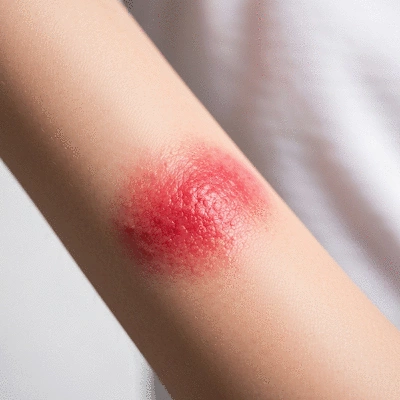
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
- Definition: Specific chronic inflammatory skin condition.
- Common Types:
- Atopic Dermatitis
- Contact Dermatitis
- Dyshidrotic Eczema
- Stasis Dermatitis
- Causes: Genetic (FLG, CARD11) & environmental triggers.
What if understanding your skin could lead to a more comfortable life? Knowledge about conditions like eczema and chronic rashes empowers you to take control of your skin health.
Understanding the unique characteristics of eczema and chronic rashes is crucial for effective management. This visual highlights their core differences and common types.
When talking about skin issues, it’s essential to understand the distinctions between eczema and chronic rashes. Both can cause discomfort and confusion, but they have different characteristics and treatment approaches. Eczema is a specific condition that often presents as red, inflamed patches on the skin, while chronic rashes can encompass a broader range of skin irritations that persist over time. Let’s break these down further to clarify the differences.
Eczema, often referred to as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that may flare up periodically. It commonly occurs in children but can persist into adulthood or even appear later in life. The types of eczema include atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, and more. Understanding these variations helps in identifying the right treatments tailored to individual needs.
Eczema can manifest in several forms, each with unique symptoms. Here’s a brief overview of the most common types:
Each type requires a different approach for management, emphasizing the importance of accurate diagnosis. As someone passionate about skin health, I believe identifying these distinctions early can lead to more effective treatment outcomes for individuals.
Chronic rashes can be more challenging to define since they encompass a variety of skin conditions that persist over time. Unlike eczema, chronic rashes may not have a singular cause or appearance. They might be linked to ongoing irritants or allergies, and can include conditions like psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis.
Recognizing the symptoms of chronic rashes is crucial for effective management. As I always emphasize at What Are Rashes, being proactive in understanding your skin can lead to better health outcomes and a more comfortable daily life.
To better manage your eczema or chronic rash, consider incorporating a consistent skincare routine tailored to your skin's unique needs. Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products to minimize irritation, and always patch-test new treatments. Keeping your skin hydrated and protected can significantly reduce flare-ups and improve overall skin health.
Eczema is a specific chronic inflammatory skin condition with various types (e.g., atopic dermatitis), often linked to genetic and environmental factors. Chronic rashes are a broader term for any persistent skin irritations that can have diverse causes and appearances.
Common types of eczema include Atopic Dermatitis (the most prevalent form), Contact Dermatitis, Dyshidrotic Eczema, and Stasis Dermatitis. Each type has unique characteristics and often requires different management strategies.
Eczema is primarily caused by genetic factors, such as mutations in genes like FLG and CARD11, combined with environmental triggers. Chronic rashes can be triggered by various environmental factors like stress, certain foods, weather changes, and ongoing irritants or allergens. Understanding these influences can help identify and manage conditions more effectively.
Effective management includes keeping a journal to identify personal triggers, consulting with dermatologists for tailored advice, and adopting a consistent skincare routine. Using fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products and staying hydrated can also significantly reduce irritation and flare-ups.
Yes, eczema can be hereditary. Research suggests that if one or both parents have eczema, their children are more likely to develop it. Genetic predispositions, such as variations in the FLG gene, play a significant role in susceptibility. For more information, you can explore resources like Medical News Today.
Absolutely. Studies indicate that household environments can significantly influence the likelihood of children developing eczema. Factors like exposure to certain allergens, pollutants, and even the cleanliness of the home can play a role. You can find more details on this topic from sources like News-Medical.net.
Understanding eczema and chronic rashes is essential for anyone affected by these conditions. The interplay between genetic factors and environmental triggers plays a pivotal role in how these skin issues manifest. From the genetic influences of specific genes like FLG and CARD11 to the detrimental effects of common environmental irritants, gaining insight into these aspects can empower individuals to better manage their symptoms.
Research highlights that recognizing these factors can lead to more effective treatment plans. At What Are Rashes, we emphasize the importance of early identification and a proactive approach, allowing individuals to feel more in control of their skin health!
When it comes to eczema, understanding its complexities can seem daunting. However, breaking it down into genetic and environmental components helps clarify its management. Here are some key points to consider:
By understanding these factors, individuals can develop a more personalized and effective strategy for managing their skin conditions. I encourage everyone to take an active role in their skincare journey!
Awareness is the first step toward effective management of eczema and chronic rashes. By being informed about the triggers and symptoms, individuals can take proactive measures. Here are some strategies I recommend:
Implementing these strategies can significantly improve the management of eczema. Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to skin health!
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article: